Osteoarthritis of the knee joint (gonarthrosis) is a lesion of the knee joint is usually not inflammatory in nature, which leads to the wear and tear of the cartilaginous layer of the knee joint and, with time, to the destruction of the cartilage deformation of the king's meadow and the restriction of mobility. Therefore, it is important to detect the disease and to know, how it is treated.
Osteoarthritis of the knee joint (called the knee – from the ancient Greek "goni" – Knee) is a progressive degenerative-dystrophic lesions of the cartilage along the surface of the joint, which leads to disruption of its work and the pain, the sensations.
Causes of osteoarthritis of the knee
Osteoarthritis is divided into primary (equal to itself) and, secondly, that arises as a result of other diseases of the knee joint.
Primary
Osteoarthritis primary (genuine) begins the arthritis of no obvious cause, and the unmodified articular cartilage in many joints at the same time. Occurs more frequently in persons over 40 years. It has also been proven that women suffer more often than men to osteoarthritis of the knee joints and the joints of the hands.
Why is primary osteoarthritis, which is not clarified until the end, but probably to metabolic disturbances lead. This causes the tissue to a change of the biochemical reactions that take place in cartilage. With time, you will be destroyed, Alliance, collect, and salt. The surface of the knee joint changes with the structure of the cartilage, causing the liquid accumulates in the king's meadow, and you will get the cyst Becker.
Secondary
It is not the result of disease or injury to the joints, according to their clinical manifestations differs from that of the primary. Developed in almost all joints.
Secondary osteoarthritis arises from the following reasons:
- Inflammatory process-immune or infectious origin;
- Dysplasia or traumatic injury to the meniscus or the knee (mini scope);
- intra-articular fractures of the bone that form the knee joint use;
- rheumatoid Arthritis;
- Tumors the bone use;
- ankylosing Spondylitis;
- Osteoarthritis arise in Paget's disease.
Symptoms

Among the symptoms of osteoarthritis are the following:
- Pain in the feet, knees, hips, the loin;
- Joint stiffness, stiffness, and crunching in the joints;
- Pain after sleep or long stay in a Position;
- Swelling of the joints;
- Pain during change of weather;
- Joint pain after exertion;
- Injuries – fractures, dislocations, and injuries of the menisci;
- the increased loads;
- overweight and obesity;
- the weakness of the ligamentous apparatus – loose Bundles;
- Violation of the metabolic processes in the body;
- Stress.
Deformity of the joint
Deformity of the joint, the change of the shape of the joint, the displacement of the ends of the bones in the joint in case of dislocation, the development of the joint pathological tissue growths is. The most common deformities of the joints of the hands, feet are exposed to the lower leg.
Misalignment of the joints is usually use by complex metabolic disorders in periarticular, bone, or cartilage tissues, where the property have been unusual in the localization and concentration of the substance
A result of the Deformation of the joints is a fusion of the joints, bony growths, subluxations of the joints and damage to the muscle and ligaments is often.
In relation to the simultaneous sign of osteoarthritis of the knee applicable to a symptomatic treatment, however, a comprehensive approach, aimed at the elimination of the disease as a whole, shows the great performance and prevents relapses.
Diagnosis of deformation of the joints is independent of the General diagnosis. It is the basis of further investigation and General results. The objective examination of the joints, facilitates their configuration, determine, swelling, pain at the feeling and movements, the volume of active and passive movements in the joints and changes in the skin and under the skin in the area of the joints.
Restriction of the mobility of the joint
Mark different degrees of restriction of the mobility: from easy, hardly noticeable against the usual quantity of the movement, up to complete loss of mobility.
To distinguish according to the degree of restriction of the mobility of the joint:
- Ankylosis – full immobility in the diseased joint.
- Rigidity – are stored only a limited amount of movements. For example, a small rocking movement. In the investigation of the rigidity should be distinguished from ankylosis.
- Contracture – restriction of mobility, and a significant, but still remains a certain amount of motion in the joint. Determine the volume of movements allows the knife with a simple angle.
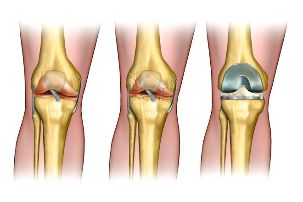
The degree of osteoarthritis of the knee
The first. In this case, the disease is characterized by slight pain at the time of committing the active movements. Can synovial fluid in the cavity of the joint, what is a cyst in the formation of Baker Pain occur during travel, but a passport in the state of rest. Damaged cartilage, but the external deformity of the joint invisible.
The second. Joint space narrowing, happens cartilaginous tissue Standard is damaging in a high degree. In the picture, there in the x-ray diagnostics, you will use notice excessive growth of bone. Sharp pain accompanied every movement in which the knee joint is involved. In the state of rest miss the sensations, but then re-appear. To pain characteristic crunch added in the Commission of extensor movements.
The Third. In places the cartilage is thin, formed blank areas of the bone. On the x-ray image, a large number of osteophytes deposits of the salts in the cavity of the joint is significantly. In addition, there is a free joint in the body can be demonstrated.
Possible complications and consequences of osteoarthritis of the knee
The osteoarthritis of the knee is a degenerative disease that progresses with time. Joint pain and stiffness are not so strong that the Patient is able to cope with daily activities. Some people lose the ability to work, if the osteoarthritis progresses to the point that the doctor recommends a surgery for the replacement of the joints.
If you ignore symptoms of the disease and timely treatment, the probability of complications is very high.
On the potential impact of the current osteoarthritis include:
- a critical deformation of the joint, and its complete destruction;
- the global limitations of motor skills;
- The Band's performance hernias;
- diminished quality of life, the loss of ability to work.
Which doctor deals with the treatment?
This is a police officer, surgeon, Internist, orthopedist can. As needed wise counsel rheumatologists. Physician-rheumatologist she examined provides an accurate diagnosis, determine which joints are affected. To prescribe laboratory and instrumental methods of diagnosis.
Only through a full examination of professional is the answer to the main question: what is the stage of osteoarthritis of the knee of the patient, and what treatment he needs.
In the presence of co-morbidities in the spine, the consultation of the nerve requires physician and vertebrologist. These professionals have rehabilitation treatment while continuing with pain syndrome are due to the infringement of nerve fibres in the intervertebral discs.
Diagnosis
Of diseases of the joints, similar to arthritis, cells, occur in many other diseases, and ignorant people are often wrong in the Definition of the disease. So, in any case, do not try to install the diagnosis itself.
Tool review
X-ray diagnostics – the most common and most important method due to its simplicity, accessibility and high information content. The images are usually in two projections, lateral and direct, but also a number of specific Styling.
The ultrasound examination is considered to be quite promising, to discover a liquid, an assessment of the pathologies of the surfaces of the soft parts, as well as the visualization of the cartilage and joint. Among the advantages of this method in x-ray, the possibility of the Position of the sensor, as well as the absence of the need for strict positioning of the patient for receipt of the Standard projections.
MRI and CT provide a wealth of information, as well as the possibility of a three-dimensional representation of the study area.
Laboratory analysis
Osteoarthritis of the knee pathological changes occur mainly in the articular cartilage, but also subchondral bone, synovial fluid use, other soft tissue of the joint. Because of the limited possibilities to directly examine these structures, which are an important source for the fence, biological markers, blood, urine and joint fluid.
In most of the cases in patients with osteoarthritis of the knee, no changes in blood tests and urine Tests, with the exception of the cases of Synovitis, with considerable effusion, if it does not identify elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate, hypergammaglobulinemia, and increased indicators of acute Phase CRP, Fibrinogen, inter alia, In the examination of the synovial fluid and significant differences from the normal indicators.
In the last years, an Intensive search for possible biological markers (BM) Degradation and repair of tissues of the joints (especially cartilage and bone use). BM mirrors oriented to the dynamic changes that serve as predictors for the prediction of osteoarthritis of the knee and markers of pathogenic efficacy of the treatment. The opening of new and deeper study of the well-known BM allows a better understanding of the mechanisms of the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis.
But the biggest Problem is the use of biological markers of cartilage metabolism – a result of chondro-protective properties of drugs and monitoring of treatment with drugs, the to the group of "disease-modifying".
The treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee joint
The treatment of osteoarthritis, to say the least, for example, is not the easiest task. So, before you begin your serious battle with this disease, find a good doctor, questioned him and together with him a Plan of treatment.
Drugs
The most commonly prescribed medications for relief of inflammation and pain in osteoarthritis of the knee is an anti-inflammatory drugs nesteroidna nature. Medications are effective in inflammatory processes, accompanied by Synovitis. In addition, the above-mentioned drugs relieve the pain. But they do not treat the disease itself.
When taking inflammation-inhibiting-steroidal drugs, is the cost you will comply with all recommendations of the doctor, since these drugs, there are an impressive number of side effects, especially with prolonged use.
Chondroprotectors is in a class of medications, the use of restoration of the bone and cartilage. When taking chondroprotectors is to be considered that these drugs are as effective as possible in the treatment of diseases.
Vasodilators are also in the complex treatment of osteoarthritis. With the help of them to restore the blood circulation in the joint, and spasm of the small vessels.
As an analgesic most commonly used ointments or compresses with warm effect. If it is necessary, fast relief, can the intra-articular injection of corticosteroids.
Surgery
Puncture (minimally invasive procedures). This method is applicable for the diagnosis of diseases. In the joint capsule of the needle insertion, wherein a portion of the liquid. This way, you can.the Material for the analyses, the load on the capsule, if necessary, to the input of corticosteroids directly at the site of inflammation
Arthroscopy. Is an introduction of the special apparatus of the arthroscope through the incisions in the skin. The method allows to examine carefully, to remove the joint, but also the fragments of cartilage by eliminating the cause of the inflammation and the pain.
Periarticular Osteotomy. The essence of the method consists of a submission of bone with subsequent fixation from a different angle. The Operation reduces the load on the joints and eliminate the pain over a longer period of time. In spite of its effectiveness, is applied to this type of surgery rarely is the load on the body of the patient and long lasting the duration of the Rehabilitation.
Arthroplasty. In those cases, when other treatments have not helped, the disease completely or almost completely destroyed joints, replace prostheses made of plastic, metal or ceramic.
Arthroplasty – a serious and expensive surgery requires a longer Rehabilitation. Many patients in pain within a few months after the Operation. However, this method is often the only Alternative, immobility of the patient. The life of modern prostheses reached twenty years, and in all these years, the Patient can live a full life.

The recommended diet
Diet in the first line is required in order to control your weight. It is proved that the osteoarthritis usually develops more difficult tolerated, and especially in the case of people with obesity, so:
- Restrict your consumption of alcohol, fatty foods, semi-finished products;
- You can control the Regime of a food;
- you can reduce the amount of salt;
- reduce the amount of sweets;
- Eat more and fruit (preferably seasonal).
Measures for the prevention of osteoarthritis
The most important measures to prevent the development of osteoarthritis of the knee are:
- Reduction of overweight;
- Increase of movement activity;
- the proper diet;
- compliance with the principles of the HLS.
Maintaining a healthy way of life, you strengthen your body, improve use of the condition of the cartilage, joints and bone. To advise against is from alcohol and Smoking. A lot of time in the fresh air, experience less Stress and hurry to come, a lot of good mood and positive.
Osteoarthritis – a disease that cannot be cured completely, but their development can stop when the time to pay attention to your health and to start the treatment. Therapy to reduce or even remove completely some of the symptoms, to be significant in the lives of sick people easier.


















